Buy and assign to
multiple learners
Instant access
via email link
Instant certificate
via email
Further Information - Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow Training
Description
Who is the course for?
This Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow Training course is aimed at individuals working in the chemical industry who require an understanding of heat transfer processes. It is particularly suited to those who are new to the industry and do not have a background in chemistry.
Is previous experience required?
It is expected that as a participant in this course you will have received formal training in your designated role and that you hold suitable qualifications.
How will the course benefit me?
Heat transfer is one of the most common unit operations within the chemical industry. This course will provide a comprehensive overview of heat transfer operations and the systems used for transporting and controlling fluid flow.
The knowledge gained in this course will help you understand the need to follow procedures and will enable you to carry out heat transfer operations in a safe manner. You will learn about the various health and safety hazards involved in such operations and how these can be controlled.
How will the course benefit my company?
By ensuring that you are fully aware of the potential hazards involved in heat transfer and fluid transfer operations, you contribute to the safety of the asset, your fellow workers and yourself. A reduction in incidents means a safer working environment for everyone.
What standards are referenced in the course?
This course does not refer to specific legislation or laws but is written to current HSE guidelines, industry best practice and standard operating procedures.
Is there an assessment?
Once you have completed the course, you will be asked a series of questions to check your knowledge and understanding. These are based on the learning objectives for the course and have a pass mark of 80%.
Learning Objectives
• Define heat transfer
• Define heat flow
• Describe the foundations of heat transfer and fluid flow
• Explain the importance of heat transfer and fluid flow
• Identify the three modes of heat transfer
• Describe the three modes of heat transfer
• Identify the factors that determine the rate of heat transfer by conduction
• Explain the significance of factors that determine the rate of heat transfer by conduction
• Define Fourier’s law
• Demonstrate how Fourier’s law can be used to calculate steady state heat transfer through simple layers of material
• Explain why the rate of heat transfer will be resisted and reduced under practical conditions
• Explain the difference between natural and forced convection
• Identify the advantages and disadvantages of natural and forced convection
• Identify the factors that determine the rate of heat transfer by natural and forced convection
• Explain the significance of the factors that determine the rate of heat transfer by natural and forced convection
• Identify the factors that determine the rate of heat transfer by radiation
• Explain the significance of the factors that determine the rate of heat transfer by radiation
• Identify the reasons for restricting heat losses from the hot surfaces of industrial processing equipment
• Explain the reasons for restricting heat losses from the hot surfaces of industrial processing equipment
• Identify the factors that affect the rate of heat loss from the hot surfaces of industrial processing equipment
• Identify the factors that affect the rate of heat loss from hot surfaces by convection and radiation
• Explain the significance of the factors which affect the rate of heat loss from hot surfaces by convection and radiation
• Identify the methods of minimising heat losses from hot surfaces
• Describe the methods of minimising heat losses from hot surfaces
• Identify some common lagging materials used
• Describe the insulating properties of those common lagging materials
• Identify the main components of heat exchangers
• Describe the construction of the main components of heat exchangers
• Describe the operating principles of the main components of heat exchangers
• Identify the different types of heat exchange equipment
• Describe the function of the different types of heat exchange equipment
• Explain the effects of scaling, fouling and corrosion on the efficient operation of heat exchangers
• Explain why heat exchangers need to be regularly cleaned
• Identify some common heat exchange fluids
• Describe the applications of these heat exchange fluids
• Identify the advantages and disadvantages of these common heat exchange fluids
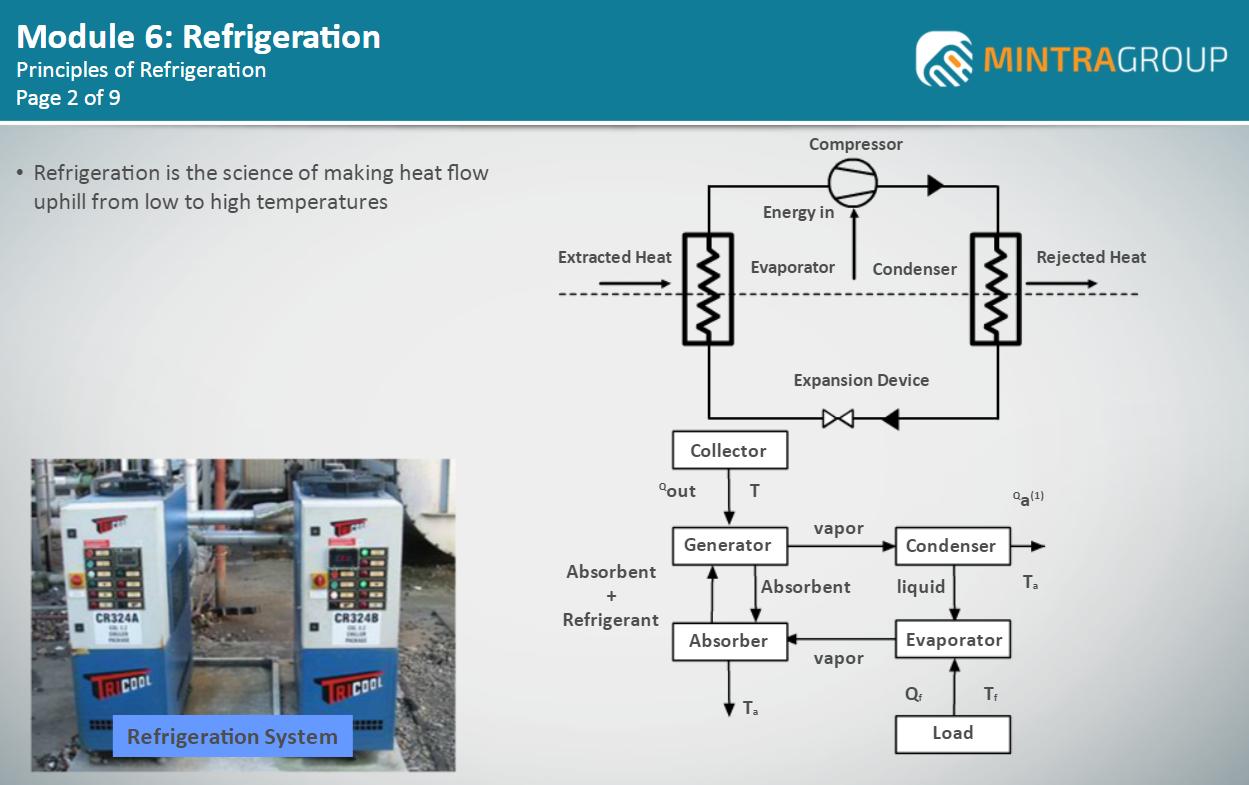
• Identify the basic principles of refrigeration
• Explain the basic principles of refrigeration
• Identify the components of a vapour refrigeration system
• Explain the functions of the vapour refrigeration system components
• Explain the difference between primary and secondary refrigerants
• Identify the functions of primary and secondary refrigerants
• Identify some primary and secondary refrigerants and their properties
• Identify the methods of minimising hazards from hot surfaces
• Describe the methods of minimising hazards from hot surfaces
• Identify the hazards associated with heat exchange fluids
• Identify the precautions that will minimise the hazards associated with heat exchange fluids
• Identify the hazards associated with refrigeration systems
• Identify the precautions that will minimise the hazards associated with heat refrigeration systems
• Identify the factors which affect the flow of fluid in pipes and tubes
• Explain the significance of the factors that affect the flow of fluid in tubes and pipes
• Define Reynolds number
• Explain the significance of Reynolds number in pumping and heat transfer operations
• Demonstrate how you would calculate Reynolds number for a given set of conditions and predict fluid flow
• Explain the difference between Newtonian and non-Newtonian flow
• Define Bernoulli’s theorem
• Identify the different terms used in Bernoulli’s theorem
• Explain the significance of the terms used in Bernoulli’s theorem
• Explain how you would use Bernoulli’s theorem to solve problems relating to fluid flowing in pipes
• Explain how Bernoulli’s equation must be modified before it can be used to solve project design problems
• Demonstrate how you would calculate the power and energy requirements for pumping fluids against the pressure and heat of the liquid
• Explain the concept of optimum pipe diameter
• Describe the process of cavitation
• Explain the effect cavitation has on pump efficiency
• Define net position suction head
• Explain the significance of net position suction head
• Explain the significance of pump capacity
• Define volumetric efficiency
• Explain the significance of volumetric efficiency
• Describe how centrifugal pumps are constructed
• Explain how centrifugal pumps operate
• Identify the applications of centrifugal pumps
• Describe how positive displacement pumps are constructed
• Explain how positive displacement pumps operate
• Identify the applications of positive displacement pumps
• Identify the factors that influence the type of pump chosen for a particular duty
• Describe the factors that influence the type of pump chosen for a particular duty
• Demonstrate how you would select and justify a pump for a given duty
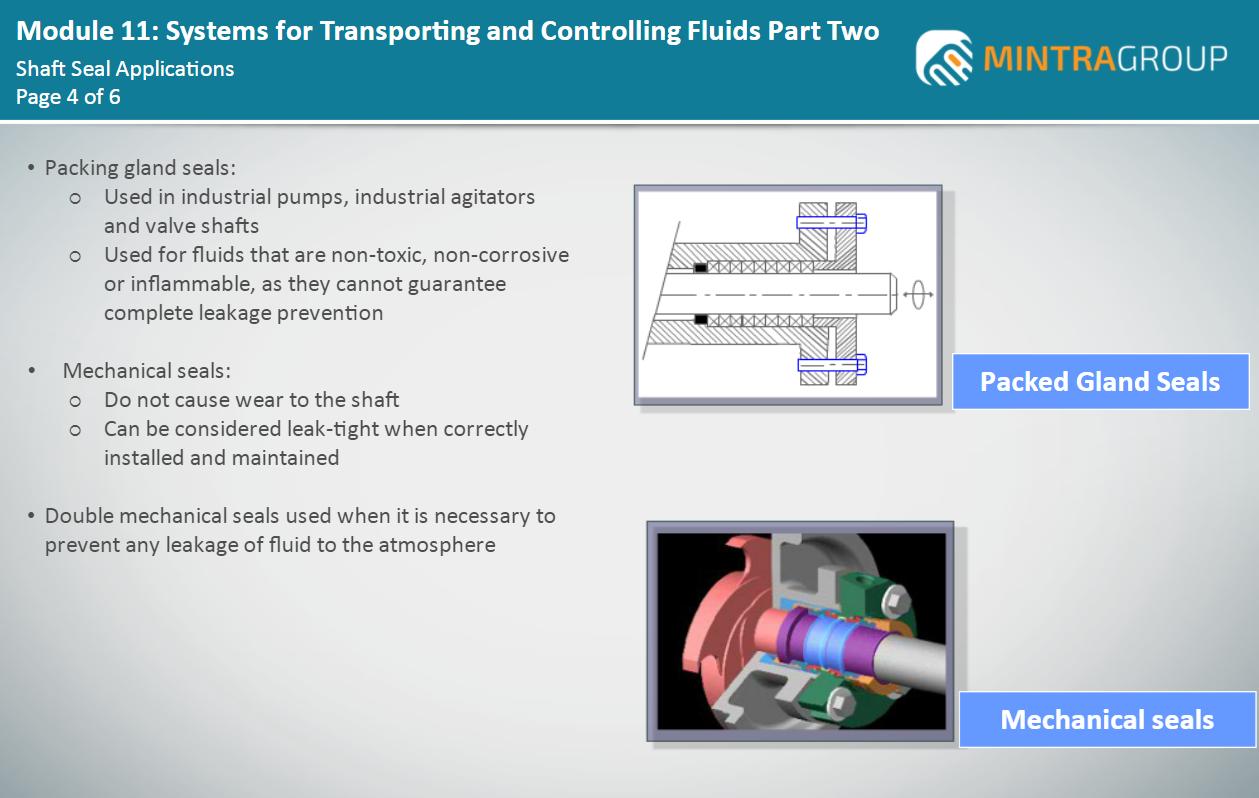
• Explain why pump drive shaft seals are required
• Identify some common shaft seals
• Describe how these common shaft seals are constructed
• Identify the applications of these common shaft seals
• Explain the need for lubrication of shaft seals, bearings and other moving parts
• Describe how pumps used to transfer gases are constructed
• Explain how pumps that are used to transfer gases operate
• Identify the application of pumps used to transfer gases
• Identify the methods of preventing the deposition of solid material in pipelines
• Describe the methods of preventing the deposition of solid material in pipelines
• Identify some common methods of cleaning pipelines
• Describe the common methods of cleaning pipelines
• Identify the hazards associated with the transfer of flammable, toxic or corrosive materials
• Describe the hazards associated with the transfer of flammable, toxic or corrosive materials
• Identify some precautionary measures that can be used to prevent hazards from arising
• Identify some devices that are used to minimise dangers that arise from the excessive build-up of pressure in pipelines
• Describe those devices that are used to minimise dangers that arise from the excessive build-up of pressure in pipelines
• Describe the start-up procedures for centrifugal and positive displacement pumps
• Describe the shutdown procedures for centrifugal and position displacement pumps
• Identify the hazards associated with the cleaning of pipes
• Describe the hazards associated with the cleaning of pipes
Assessment
Once you have completed the course, you will be asked a series of questions to check your knowledge and understanding. These are based on the learning objectives for the course and have a pass mark of 80%.
System Requirements
• Internet access - users will need a device with a web browser and internet connection
• System - runs on computers, tablets and mobile devices using Windows 7 and above and MAC OS devices running IOS 11 and above
• Browsers - Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari
• Minimum browser size - none
• Audio - requires device speaker or headphones
Recommended Courses
Reviews
Insights & News
At Mintra, we're so much more than just a team—we're a force driving innovation and excellence in maritime training across Europe.
We’re excited to be taking the stage at one of Europe’s leading showcases of organisational learning.
We are delighted to share the exciting news that our People and Culture team has been shortlisted for the prestigious cHeRries Awards!